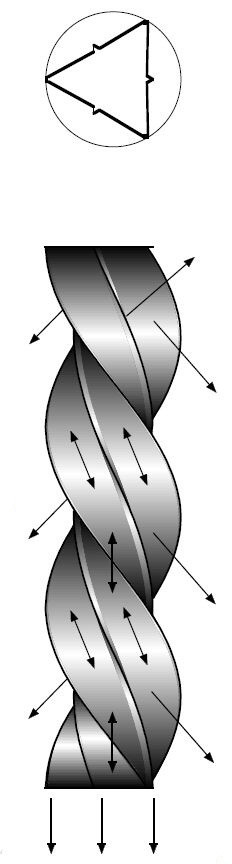
Micropile shape - the spiral shape provides many times larger friction area than an ordinary tube-type micropile. When installed by ramming, it is gradually screwed in and compresses (compacts) the adjacent soil. Spiral shape of wings provides support forces in all directions. The load induced, whether in pressure or tension, is distributed evenly over the total pile length.
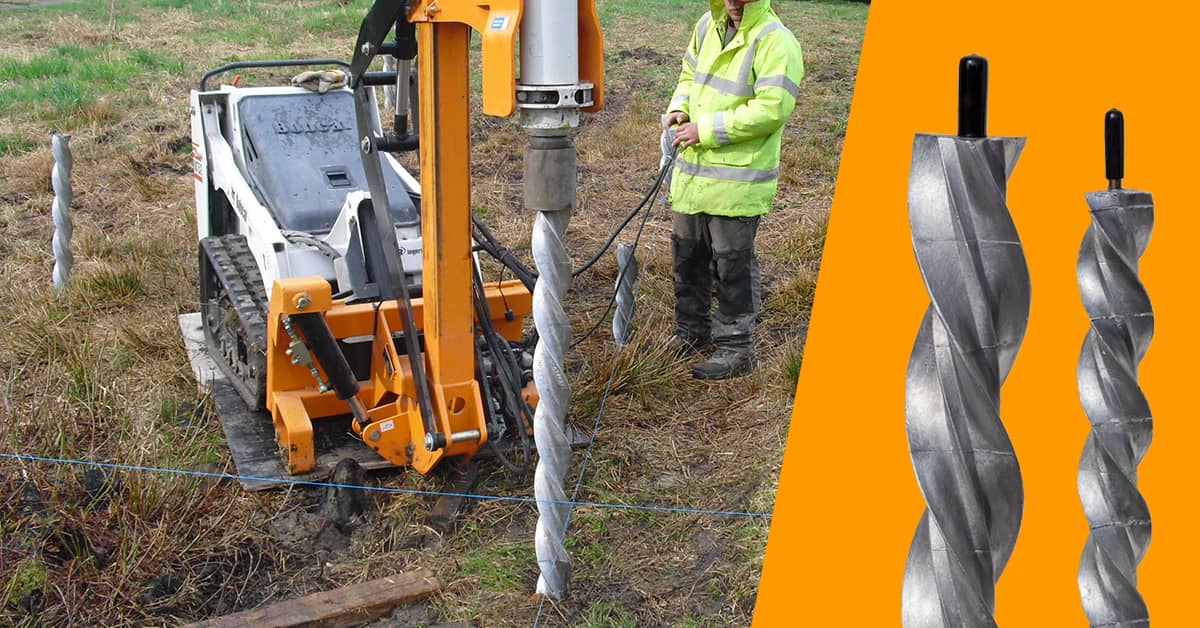

Micro-pile
Use of STATIpile micropiles
Increasing load capacity of partially collapsed foundations
STATIpile was initially developed for light repairs of foundation structures with disturbed static and difficult access. In combination with helical supports, the whole system is suitable for complete repairs of buildings with faulty foundation structures and cracked masonry walls. The repair is very quick, restricts the use of the building in the course of repair works to the minimum extent, and it is affordable.
Fixing additional foundation setting
In foundations, STATIpile micropiles may also be used to increase the load capacity of the foundation in case of various extensions and load changes to original foundations.
New foundations for steel structures
STATIpile micropiles may also be applied to support the tensile force. This characteristic can be used for stabilization of support walls, river banks, and where we may anticipate tensile phase effect (textile structures, cranes, telephone towers for GSM signal). It may also be used for foundation structures of new buildings in unfavourable places or under unfavourable foundation conditions.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is micropile?
A micropile (also known as a micro pile) is a small-diameter pile that is used to transfer load from a structure to deeper soil or rock layers with a high bearing capacity. Micropiles are typically made of high-strength steel or composite materials, and they are installed using specialized drilling equipment.
Why micro piles are used?
Micropiles are used in a variety of construction applications, including foundation repair, slope stabilization, and bridge rehabilitation. They are often used when traditional pile foundations are not feasible or when the soil conditions are not suitable for other types of piles. Micropiles are also used in cases where the loads on the structure are relatively light, as they can provide a cost-effective alternative to larger piles.
How does micro piling work?
The installation of micro piles typically involves drilling a hole to the desired depth, placing the micro pile into the hole, and grouting it in place. The load-bearing capacity of the micro pile is determined by the size and strength of the pile material, as well as the soil conditions and the design load.
What is the difference between bored pile and micropile?
The main difference between a bored pile and a micropile is the size of the pile. Bored piles are typically larger in diameter than micropiles and are used to transfer larger loads. They are typically installed using a bored pile rig, which removes soil from the ground using a drilling tool and then replaces it with concrete or another load-bearing material. Micropiles, on the other hand, are installed using smaller, specialized drilling equipment and are used to transfer smaller loads.
Micropiles parameters
| Typ | r 60 mm STATIpile | r 100 mm STATIpile |
|---|---|---|
| Length | 1 m | 1 m |
| Material | Legierung AlSi7Mg0,3 | Legierung AlSi7Mg0,3 |
| Screw thread | M12 | M20 |
| Standard | DIN975 | DIN975 |
HAVLOVA KNIHOVNA – LORETÁNSKÉ NÁMĚSTÍ
GMUNDEN RAKOUSKO – ZÁKLADY PRO PŘÍSTAVBU RD
MIKROPILOTY – TISKÁRNA TRIANGL PRAHA
MIKROPILOTY KOLBENSCHMIDT ÚSTÍ NAD LABEM
Price of micropile STATIpile
Fill in the inquiry form for the price offer.
| r 60 mm STATIpile | r 100 mm STATIpile | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ground | Class | SPT | Tensile force (kN) | Pressure (kN) | Tensile force (kN) | Pressure (kN) |
| Dirt with medium plasticity | F5 | 0 - 5 | 5 | 8 | 7 | 10 |
| Clay with high plasticity | F7 | 1 - 4 | 7 | 10 | 10 - 20 | 15 - 25 |
| Clay with medium plasticity | F6 | 4 - 8 | 10 - 15 | 15 - 20 | 25 - 35 | 30 - 40 |
| Clay with low plasticity | F6 | 8 - 20 | 25 - 30 | 30 - 40 | 40 - 60 | 70 - 90 |
| Sandy clay | F4 | 1 - 4 | 7 | 15 - 20 | 12 - 15 | 15 - 20 |
| Gravel with soil admixture | G3 | 20 - 40 | 10 - 20 | 30 - 40 | 15 - 30 | 40 - 60 |
| Gravel with good grain size | G1 | 30 - 50 | 30 - 40 | 30 - 40 | 20 - 60 | 150 |
| Clay | 50 + | 50 | 50 | 150 | 150 | |
| Silty clay | 20 + | 50 | 50 | 150 | 150 | |
| Piles leaning in the rock massif | 50 + | 50 | 50 | 150 | 150 | |










